[ad_1]
A new analysis shows that the number of antibiotics used by patients in North Africa and the Middle East has increased sharply, far exceeding the global average, which has raised concerns about the escalating risk of drug resistance to the treatment of bacterial infections.
Data-drawn by the British “Financial Times”, by the University of Oxford and Published on “The Lancet Planetary Health” — Estimate the consumption of antibiotics in 204 countries/regions between 2000 and 2018. It shows that the use of antibiotics worldwide has increased by 46%, and the use of antibiotics in countries such as Sudan, India and Vietnam has surged.
Although many poorer countries are unable to obtain adequate antibiotics and cause unnecessary deaths due to lack of appropriate treatment, the use of antibiotics in other middle- and higher-income countries far exceeds global standards.
The study, based on a combination of prescription data and statistical models, shows that the highest consumption rate in a single country—measured as a prescribed daily dose per 1,000 people per day—is in Greece, which is close to 45.9, compared to a global average of 14.3 and an average of 21.1 in Western Europe.
There has also been a sharp rise in the Middle East, where antibiotics are often provided without a prescription, which may lead to the risk of drug-resistant bacteria.
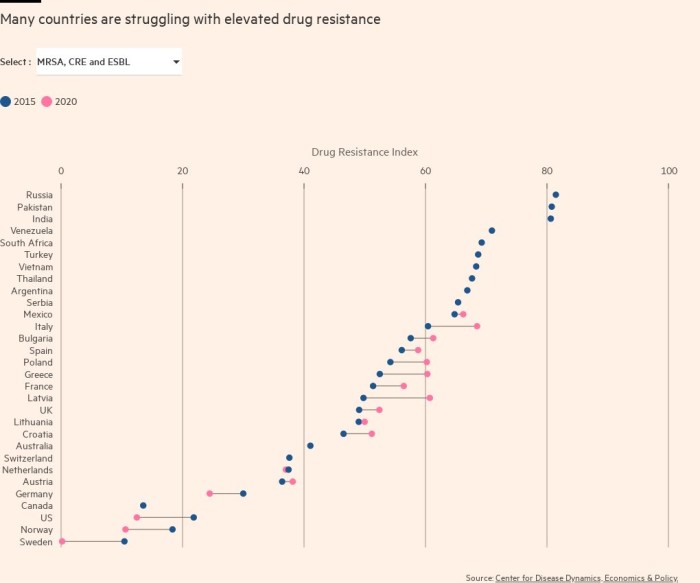
These data are contained in the data dashboard of the British “Financial Times”, which aims to track the new trend of the “silent pandemic” of antimicrobial resistance that kills hundreds of thousands of people every year.
The dashboard is designed to map the growth of disease, drug use, and corporate, government, and other response efforts.
this Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics and Policy Attempts are also made to calculate the extent of antibiotic use, and new research is underway to link consumption with the overall estimate of the burden of antimicrobial resistance.
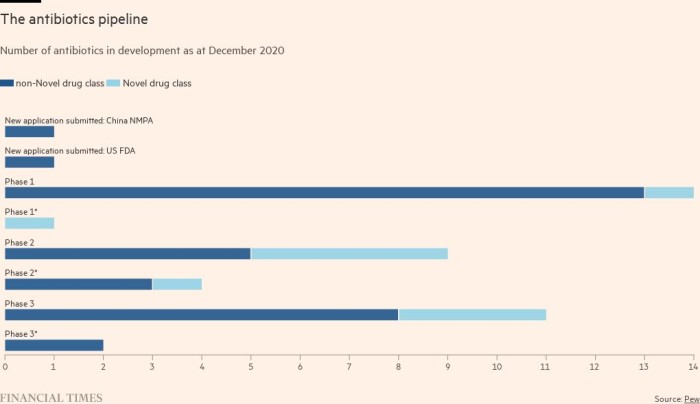
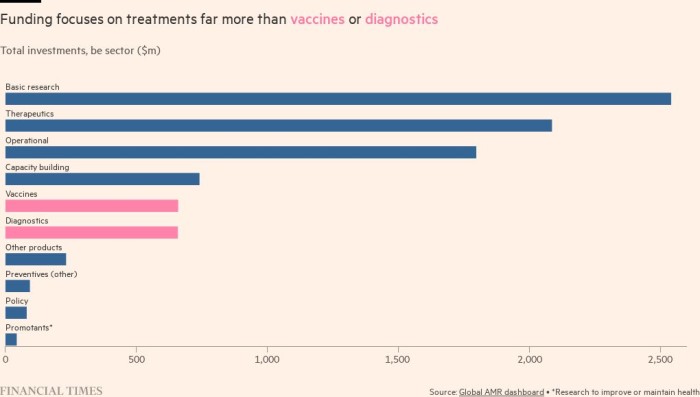
Compared with the funding and level of R&D activities dedicated to other disease categories (such as cancer), The pipe is very thin Used in the diagnosis of new antibiotics to help their targeted use, and vaccines used to prevent infection.
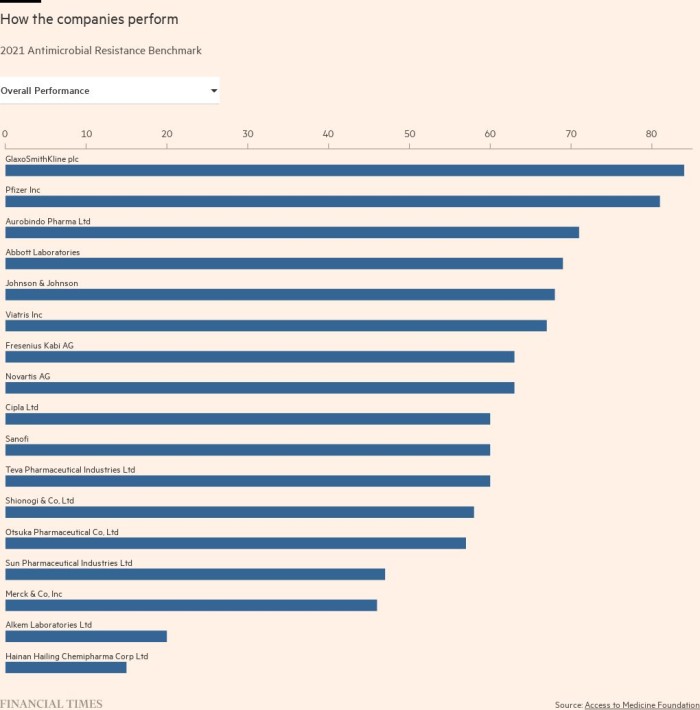
The annual benchmark test is conducted by Enter the Medical Foundation Highlights the different efforts made by innovative and generic drug companies to address antimicrobial resistance in a series of activities, including research, monitoring, and manufacturing.
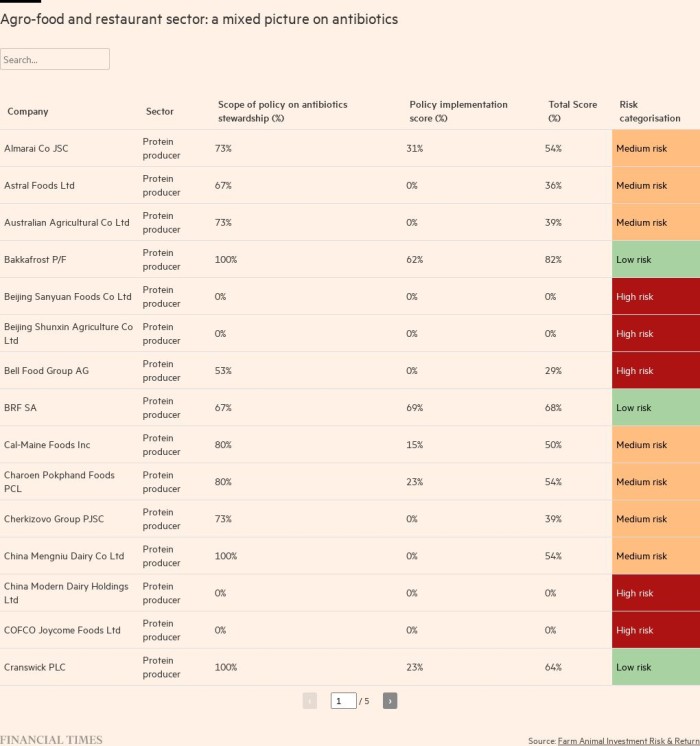
Analyst Farm animal investment risks and returns -A part of a think tank aimed at mobilizing activist investors to reduce the use of antibiotics in animals-highlighting variable responses in the agri-food and catering industries.
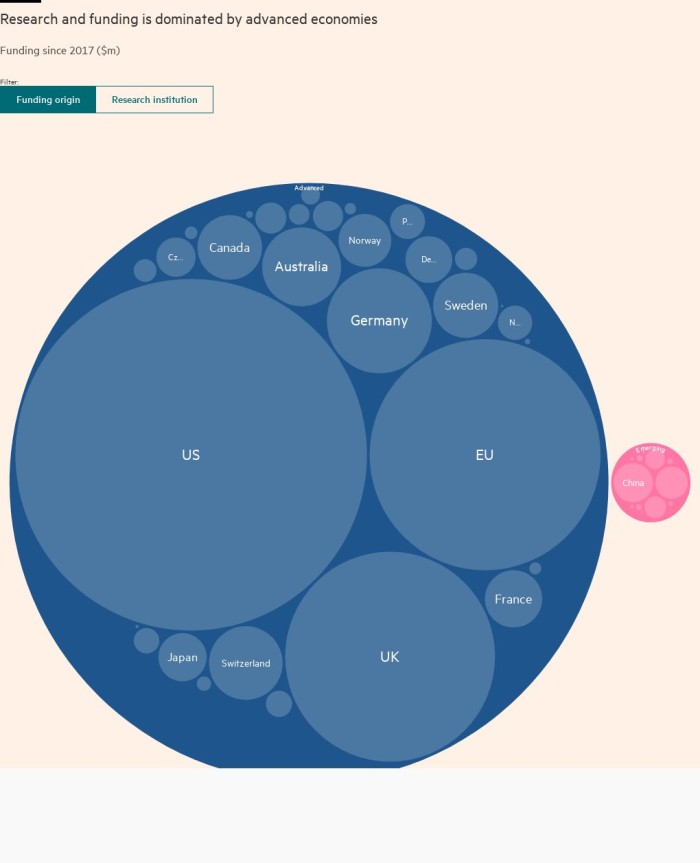
The government and other funders have increased their support for research on this topic, but have adopted widely different approaches and levels of commitment, such as Global AMR R&D Center.
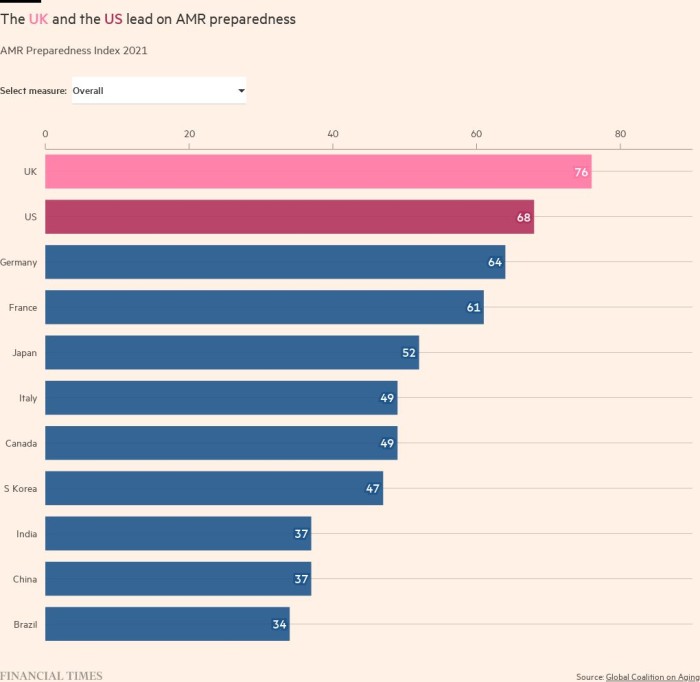
The broader efforts of countries to improve management through improved diagnosis and infection control measures have also changed a lot, just as the Global Ageing Alliance’s global AMR Readiness Index.
[ad_2]
Source link